2025年12月5日上午,由土壤与农业可持续发展全国重点实验室发起并主办的首届五色土前沿讲坛在中国科学院南京土壤研究所成功举行。
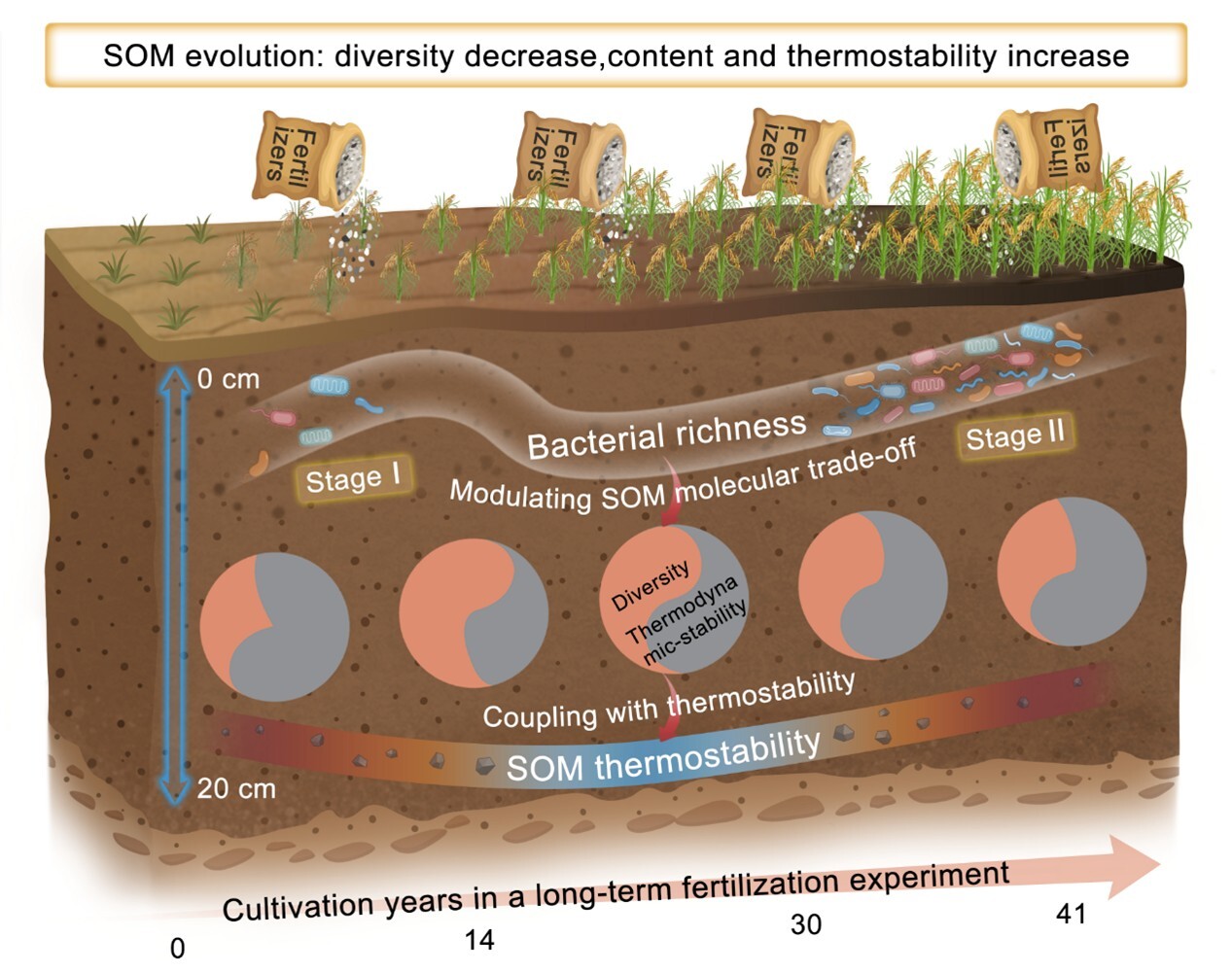
本研究借助南京土壤研究所鹰潭红壤站30多年的稻田长期定位试验和黑龙江农科院40多年的黑土长期定位试验的不同施肥处理的时间序列土壤样本,结合热重分析、傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱与微生物高通量测序技术。
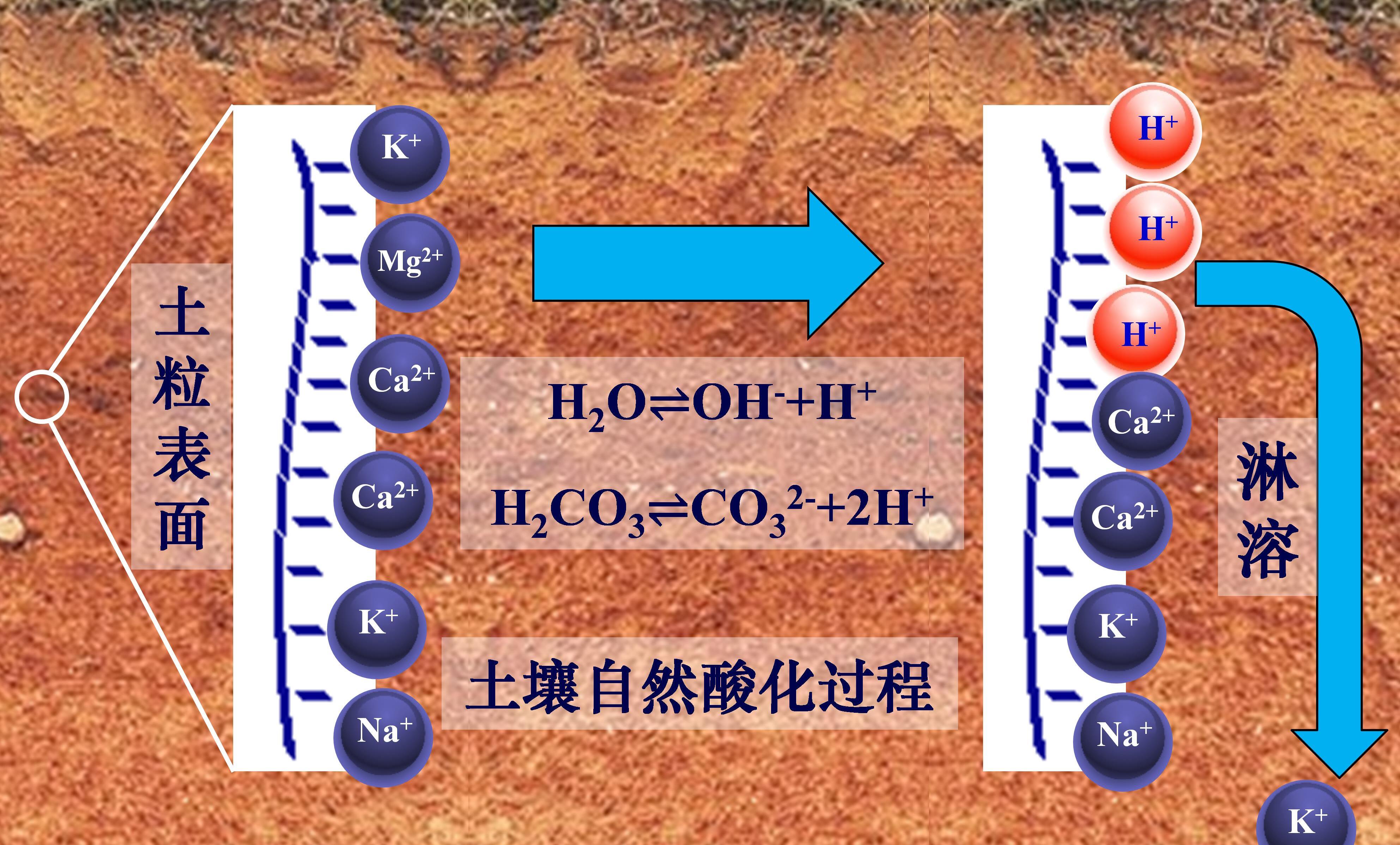
土壤中的盐基阳离子指正二价的钙和镁及正一价的钾和钠(Ca2+、Mg2+、K+、Na+),它们大部分通过静电吸引作用吸附于土壤固相表面,这也使得带负电荷的土壤表面保持电中性状态,这部分盐基阳离子称为交换性盐基阳离子。小部分盐基阳离子存在于土壤溶液中,