为了维持水稻稳产、高产,亚热带红壤区稻田磷肥投入水平一直较高。由于红壤富含铁铝,对磷的固定较为强烈,因此红壤水稻土磷盈余明显。磷的盈余一方面带来严重环境问题,另一方面深刻影响土壤生态过程。但是磷盈余如何影响红壤水稻土微生物多样性和群落组成目前仍不清楚。
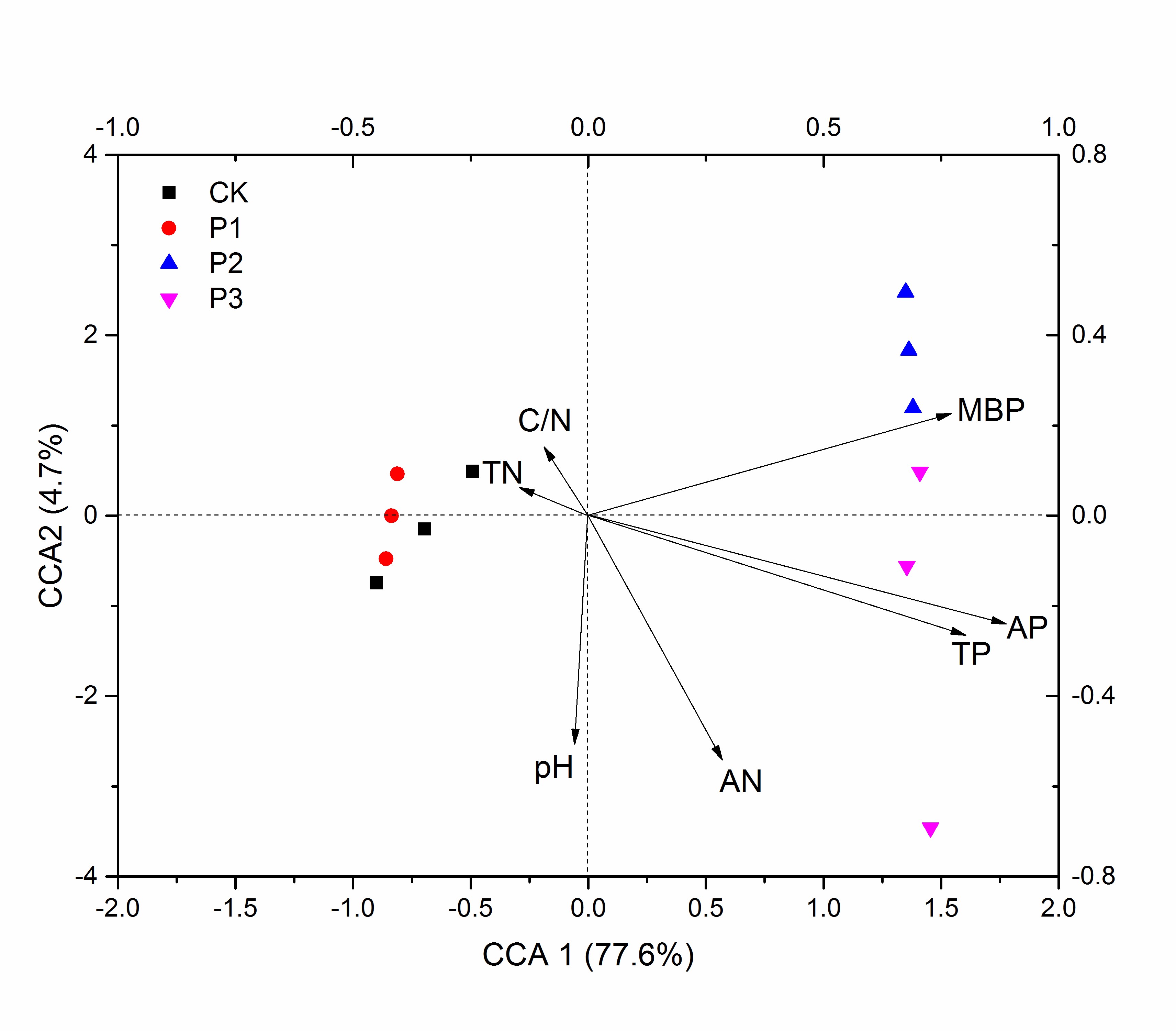
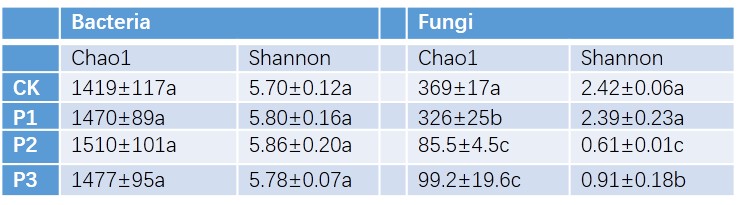
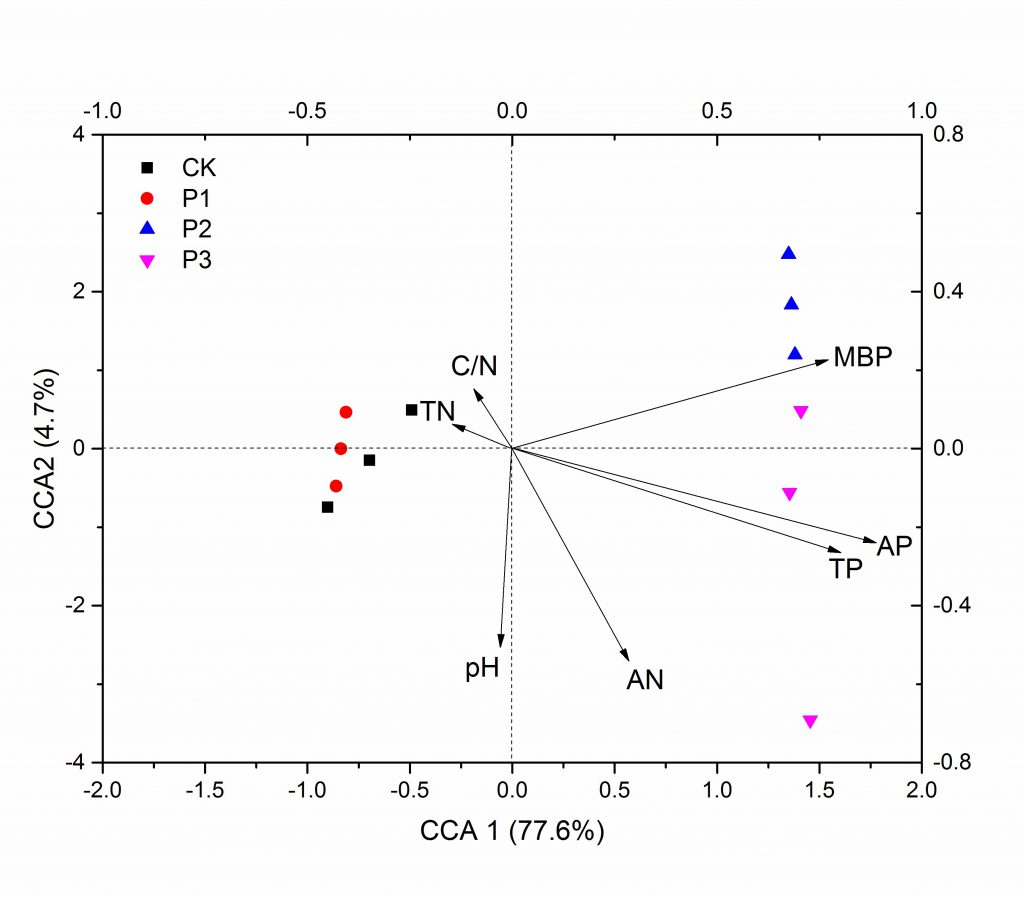
我室李忠佩课题组针对亚热带红壤区典型水稻土,通过设置不同施磷梯度室内培育试验,结合高通量测序,研究了红壤水稻土细菌和真菌多样性以及群落组成对施磷水平的响应。结果表明,不同施磷梯度对细菌α多样性和群落组成没有明显影响。过量施磷条件下,真菌丰富度指数和多样性指数显著降低。速效磷(P = 0.001), 全磷 (P = 0.002), 和微生物量磷(P = 0.005)是影响真菌群落组成的关键因素。53.6mg/kg是造成真菌群落变化的关键速效磷阈值,当红壤水稻土速效磷高于53.6mg/kg时,Penicillium和Trichocomaceae减少,但是Pseudogymnoascus和Geomyces 增加;过量施磷条件下,真菌在土壤有机质转化以及磷循环过程中可能起到关键作用。
Liu M, Liu J, Chen XF, Jiang CY, Wu M, Li ZP. Shifts in bacterial and fungal diversity in a paddy soil faced with phosphorus surplus. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2018, 54(2): 259-267
Abstract
Abundant phosphorus (P) has been applied to paddy fields in the red soil region of subtropical China. Microbial communities play important roles in soil nutrient cycling; however, the effects of P surplus on soil microbial diversity and community composition are still unclear. Soils collected from paddy fields in subtropical China was incubated and subjected to four P treatments: 33 kg ha-1 (CK), 66 kg ha-1 (P1), 132 kg ha-1 (P2), and 264 kg ha-1 (P3). Changes in bacterial and fungal diversity and community composition were evaluated by high-throughput sequencing. The different P rates had no significant effect on bacterial diversity, whereas fungal richness and diversity indexes declined significantly by increasing P rates. Principle coordinate analysis (PCoA) also indicated a shift in fungal community composition when P rates were higher than 132 kg ha-1. Available P (AP) was the dominant factor affecting fungal community composition as evaluated by canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). Multivariate regression trees (MRT) revealed that the key threshold of 53.6 mg kg-1 of AP divided treatments into two distinct groups. Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) showed that abundances of Pseudogymnoascus and Geomyces increased, but those of Penicillium and an unknown genus of Trichocomaceae decreased when AP was ≥ 53.6 mg kg-1.