Lu HL, Liu ZD, Zhou Q, Xu RK. Zeta potential of roots determined by the streaming potential method in relation to their Mn(II) sorption in 17 crops. Plant and Soil, doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-3676-8
Abstract
Aim
To compare the zeta potentials of roots of 17 crops measured with streaming potential method and to test feasibility of this method for different plants.
Methods
In addition to zeta potentials, surface charge and cation exchange capacity (CEC) of plant roots were measured independently. Mn(II) chemical forms sorbed on the roots were separated using sequential extraction.
Results
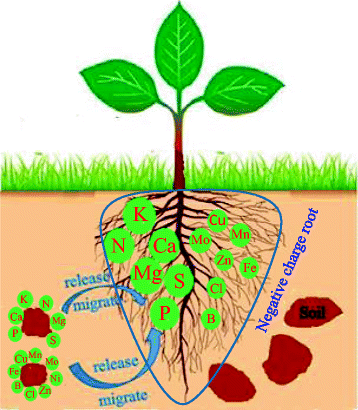
There was a significant positive correlation between the zeta potential, CEC and negative charge of plant roots, indicating that the zeta potentials of plant roots as measured by streaming potential method were reliable. The roots of legumes carried greater negative charge than did non-legumes, which was responsible for more exchangeable and complexed Mn(II) sorbed on legume roots. In the infrared spectroscopy, the intensity of absorption peaks of legume roots was higher than that of non-legume roots. This indicated a higher concentration of functional groups on the roots of legumes than those of non-legumes, which was the main reason for the greater CEC and more negative zeta potential of legume roots and their higher sorption of Mn(II) when compared with non-legume crops.
Conclusions
Surface charge properties of plant roots determined their sorption capacity for Mn(II) and chemical forms of Mn(II) on the roots.